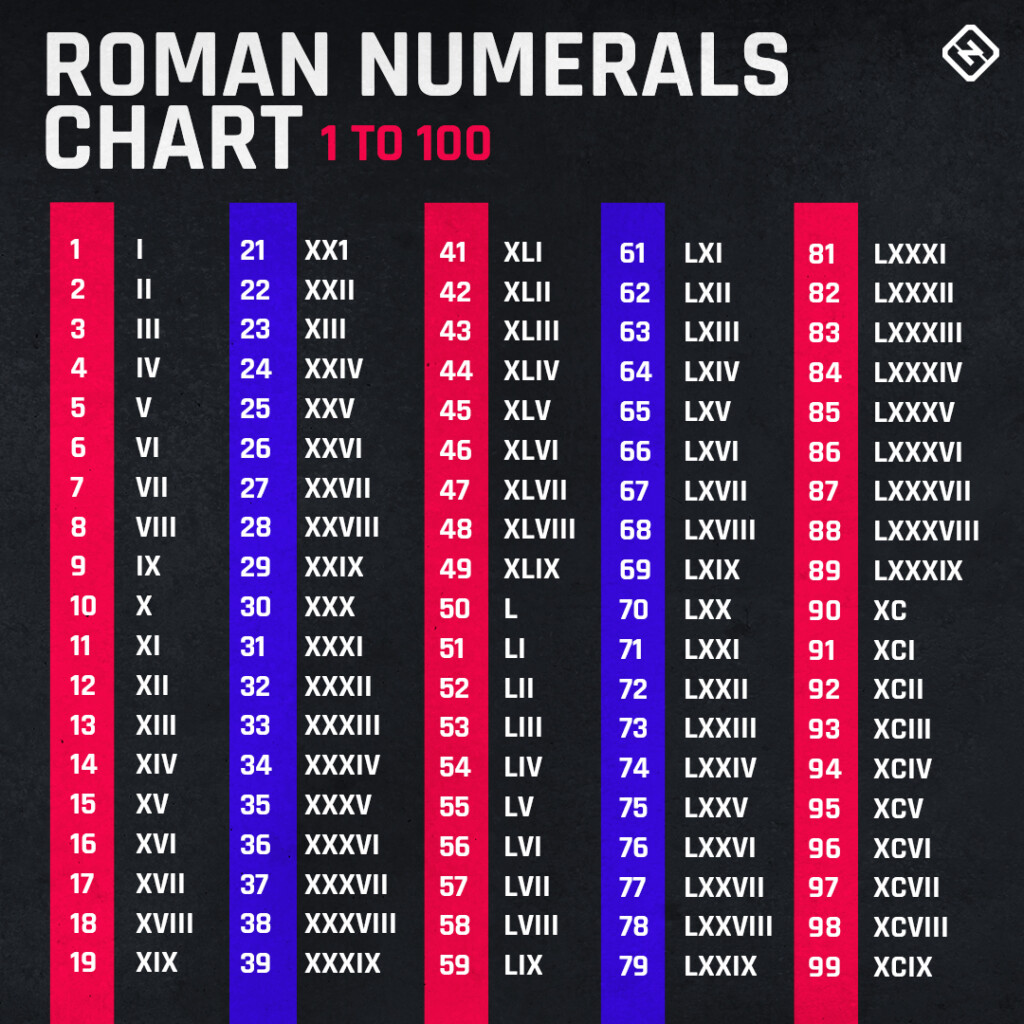
Roman Numbers Explained – Roman numerals are used throughout Europe for writing numbers. From the beginning of the Middle Ages, they were the norm after their invention in the early days of Rome.
Additional
The Roman numerals, a standard set for symbols in mathematics are employed. The letters need to be put in the correct sequence to yield the desired outcomes. They are utilized to compute an additive number without using a Zero or to represent a number, such as a book chapter number.
Romans employed math to manage military records and plan construction projects. Roman-inspired count boards were used all over Europe from the Middle Ages.
As the Romans grew older, they could utilize more complicated systems that included more complicated division and multiplication. They used decimal systems that comprised 10 numerals plus four letters. These were the same ones that went into making the abacus, a gadget with glass counters as well as beads.
The abacus was one of the most complicated systems of computation. It organized the numbers left to right in a way that made sense. It was not capable of performing long division.
Subtraction
Roman numerals have many uses. They employ symbols to represent the base number in subtractive schemes. These numbers are usually used to count, show the hierarchy of connections, and also to indicate dates. They are also utilized in photography to mark different brightness levels.
Romans used to represent numbers using an abacus. The abacus was a familiar object. The device was used to calculate military finances and also to count. For example three unciae could be a quarter of the Roman army.
The Roman numeral system’s primary function was to make it easier to add and multiplication. These letters were created using the letters C Z, X and C. The symbols could not be altered as is the case with the current Abacus.
It was also simple to subtract numbers using Roman numerals. Roman numerals must follow the following that a letter with lower value must be followed by a letter at least 10x bigger. The letter’s value must also be lower than the original number.
Stairstep pattern is an fractal
Numerous patterns and shapes which resemble fractals are found in nature, including the Roman numerals-based staircase patterns. Designers, engineers, architects and others have used fractal geometric to design intricate digital designs.
Recursion, a mathematical concept that causes fractures, is known as recursion. It’s a method for solving problems. For example, to make the Dragon’s Curve you begin with U the letter that is based on squares and then repeat the procedure four times. With each iteration you expand the area between the two sides of the square.
The Sierpinski triangle is another example of recursive building. This triangle is formed from four smaller triangles of similar shape.
Fractals originated as methods of modeling physical objects. But, it’s possible to replicate vegetable forms nowadays thanks to the advancements in computational algorithms.
One of the greatest benefits is the fine-grained and intricate complexity of natural fractured branching. It has zoom symmetry, as well as its structure.
There are a variety of explanations to explain the appearance of branches that look like trees. The basic idea is that a tree needs sunlight for photosynthesis, though. A tree that has branches can provide many mechanical benefits.
Origins
Roman numerals are first discovered in Rome which was an ancient city and state. They play a number of roles in the present day. They are used to date media, among other things. They are also used in the names of kings and popes.
Roman numerals were believed to be derived from tallysticks utilized by Roman Empire shepherds to track their flocks. But their exact origins are unknown. Depending on what kind, the tenth-sheep would have an X-shaped notch on the tallystick.
Images of these were utilized even after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. Lateron, the Arabic systems replaced them. After being brought to Europe in Europe’s eleventh century and gaining wide acceptance by the 16th Century.
Roman numerals continue to be employed even when the Arabic alphabet is more practical. They are commonly found in clocks, sporting events, and the names popes or kings.