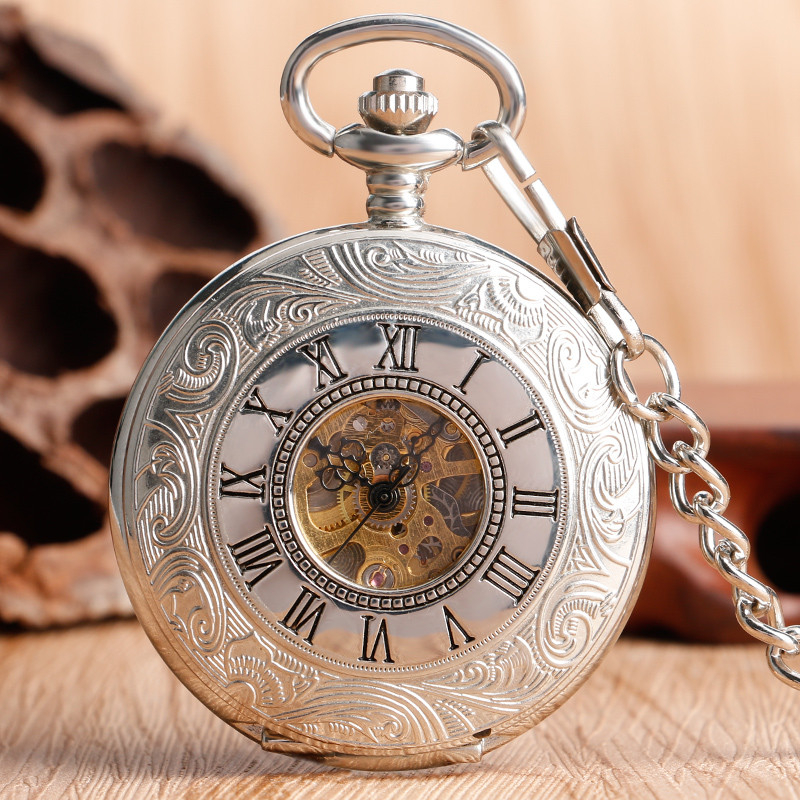
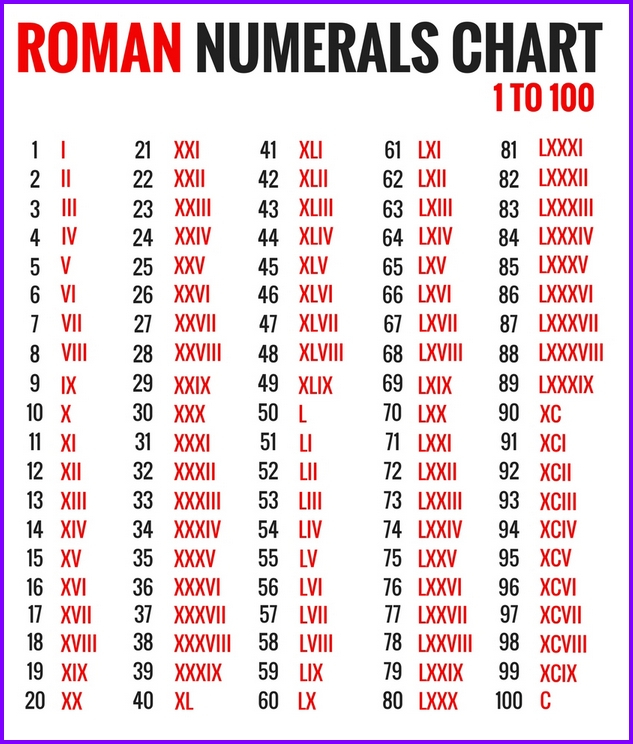
Five In Roman Numberal – Roman numerals are utilized to create numbers throughout Europe. They were the norm for writing numbers until the Middle Ages when they were created in ancient Rome.
Additional
A standard set of symbols used in mathematics are the Roman numerals. The letters need to be placed in the proper order to produce the desired results. They are used to calculate an additional number system that does not use a zero and to represent numbers, for instance book chapters.
Romans utilized maths to manage military records and organize construction projects. Prior to the Middle Ages, Roman-inspired counting boards were widely used in Europe.
As the Romans became more advanced and advanced, they could use a more sophisticated system that offered more sophisticated multiplication and division processes. They employed decimal numbers that comprised 10 numerals and four letters. These were also the ones used in the creation of the abacus. It was a device that contained glass counters, beads and calculator.
The abacus was one of the most complicated systems of computation. It organised the numbers from left to right in a way that made sense. This method did not work for long division.
Subtraction
Roman numerals have many uses. They make use of symbols to represent base numbers within a subtractive scheme. They are commonly used to count, signify hierarchical connectionsor to represent dates. These numbers can be employed in photography, however, to denote different brightness levels.
Romans used to represent numbers using an abacus. The abacus they used had the look of a popular item. The Romans utilized this device to manage their military accounts in addition to counting. Three unciae, for instance could represent a quarter of the Roman army.
The Roman numerals were created to simplify multiplication. In order to accomplish this it was the use of the letters C & X were used. But unlike modern abacus the symbols needed to be fixed, and could not be altered.
The Roman numeral system also made it simple to subtract numbers. Roman numerals demand that the lower letter is followed by a letter that is at least 10 times larger. Furthermore the letter’s value has to be less than the initial number.
Stairstep pattern that resembles an fractal
There are many patterns and designs that look like fractals in nature, such as the Roman numerals and stairstep patterns. Engineers as well as architects and designers have used geometric fractals to create intricate digital designs.
Recursion can be described as an mathematical concept that generates fractions. It is a technique that solves problems. For example, you begin with the square-based letter U and then repeat the area by four times to form the Dragon’s Curve. With each iteration, you increase the distance between the square’s two sides.
The Sierpinski Triangle is another instance of recursive architecture. The Sierpinski triangle is made up of four smaller triangles each having the same design.
Fractal notions were initially connected to the physical modeling methods. Modern computational algorithms have allowed us to replicate vegetable forms.
The fine-grained complexity of fractal branching is one of its major advantages. The fractal also displays zoom symmetry, which is a characteristic of its appearance.
There are many explanations for the appearance of branches that appear like trees. However, the basic idea is that photosynthesis occurs in sunlight. Furthermore, a tree’s branching structure is mechanically advantageous.
Origins
Roman numerals appeared in Rome as a city that was an ancient state. They play a number of roles in the modern world. They are used, for instance to date the media. They are also used on the names of popes.
Roman numerals could have been taken from tallysticks shepherds used to keep track their flocks during the Roman Empire. But their origins are an unanswered question. Based on the breed of sheep, the tenth number would be adorned with an “X”-shaped cut-out on a wooden tally stick.
These images persisted in use throughout the time that the Western Roman Empire was destroyed. The Arabic system was to soon replace the Roman system. In the sixteenth century, these numbers were gaining widespread acceptance after being brought into Europe in the eleventh century.
Roman numerals can still be utilized today, even although the Arabic system is more straightforward. They are commonly found in sporting events, clocks, and the names popes or kings.