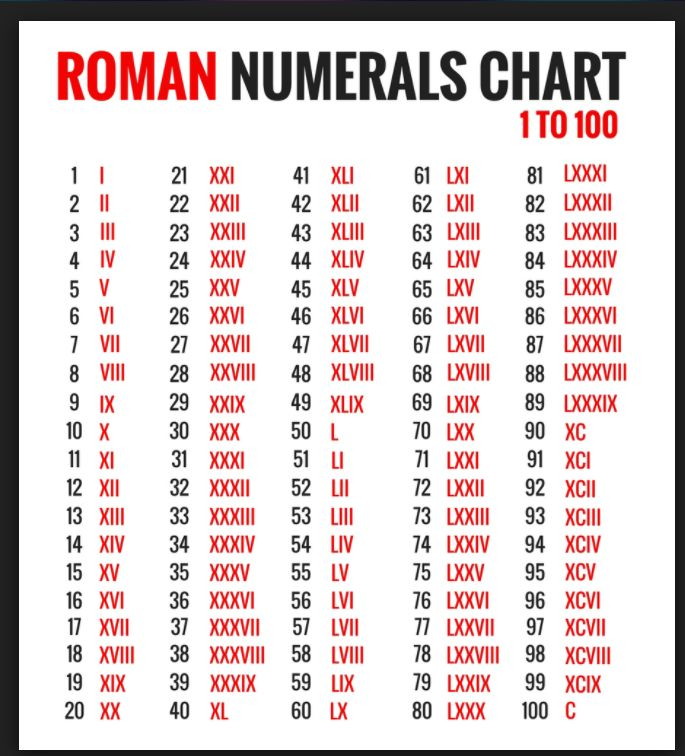
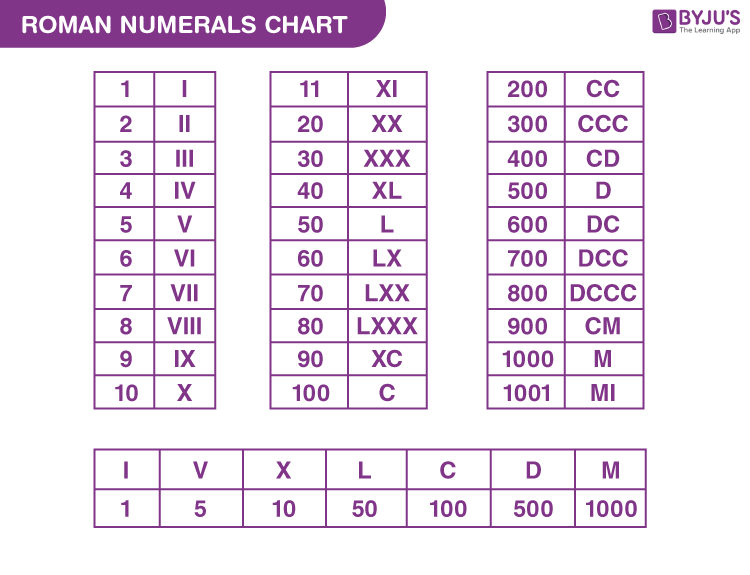
How To Write 29 In Roman Numbers – Roman numerals, which are often utilized to represent European numbers are most commonly used. Up until the end of the Middle Ages, they were the norm following their invention in the ancient city of Rome.
Addition
The Roman numerals are a common set of symbols in mathematics. To get the desired results the letters should be used in a certain order and in a fixed. They can be utilized to calculate an additive number system using a zero and also to represent numbers such as a book number.
Math was utilized by the Romans to organize their construction projects as well as manage their military records. The Roman-influenced counting tables were widespread in Europe in the Middle Ages.
As the Romans matured as they grew older, they could employ a more complex system that was more sophisticated in its division and multiplication processes. They employed a decimal system that had four letters and 10 numbers. These were also employed in the development of the calculator. It was a gadget equipped with glass counters, beads, and a calculator.
The abacus, which organized numbers left to right as it should be done it was among the most complicated algorithms of computation. Long division was not feasible with this method.
Subtraction
Roman numerals can be used in a variety of ways. They employ symbols to represent bases numbers in a subtractive scheme. Typically, these numbers are employed to count, show relationships in hierarchical order, and also to indicate dates. These numbers can be utilized in photography, however, to denote different brightness levels.
Romans represented numbers with an Abacus. The abacus they used reminded us of an object that we all have. It was used for military accounting and also for counting for the Romans. Three unciae were able to represent 25 percent of the Roman army.
The main purpose of the Roman numeral system was to facilitate multiplication and addition. The letters used were the letters C, X and Z. The symbols were set and could not be altered, as opposed to the modern Abacus.
It was also very easy to subtract numbers thanks to Roman numerals. Roman numerals demand that the lower letter must be followed with a larger letter that is at minimum 10 times bigger. Also, the letter’s original value must be less than the new one.
Stairstep pattern, like the Fractal
Many patterns and forms that resemble fractals can be found in nature, including the Roman numerals-based steps. Designers, architects, and engineers have used fragmental geometry in their designs to create complex digital works.
Recursion is a mathematical concept which creates the fractals. It is a technique used to tackle issues. For example, you begin with the square-based letter U and then multiply the area by four times to form the Dragon’s Curve. You expand the space between the square’s two sides by repeating the process.
Another example of recursive construction is the Sierpinski triangle. The triangle is comprised of four smaller triangles each with the same overall shape.
Fractals were initially connected to physical techniques for modeling. But, the most advanced technological algorithms allow for vegetable designs to be reproduced.
One of the main advantages is the fine-grained nature of fractals that are branched. It displays zoom symmetry and structural appearance.
Different fields have different theories for branches that appear like trees. The fundamental notion is that a tree needs sunlight to photosynthesis, but. A tree’s branching structure has many mechanical advantages.
Origins
Rome as a city-state from the past was the place the place where Roman numerals first came into existence. They play a number of roles in today’s world. They are used to determine the date of media, for instance. They are also included in the names of kings as well as popes.
Roman numerals could have been taken from the tally sticks utilized in the Roman Empire by shepherds to count their flocks. However, it’s not known where they came from. Depending on what kind the sheep is, it will have an X-shaped notch on the tallystick.
These images persisted in use throughout the time that the Western Roman Empire was destroyed. However, the Arabic system took over their place. In the 16th century, these numbers had gained widespread acceptance after they were introduced into Europe during the 11th century.
While the Arabic system is simpler to grasp, Roman numerals still have an importance in contemporary times. They are frequently used in sports events, clocks, and the names popes or kings.