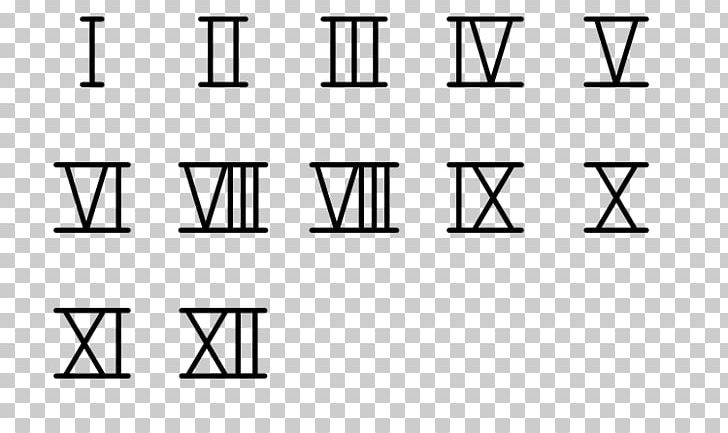
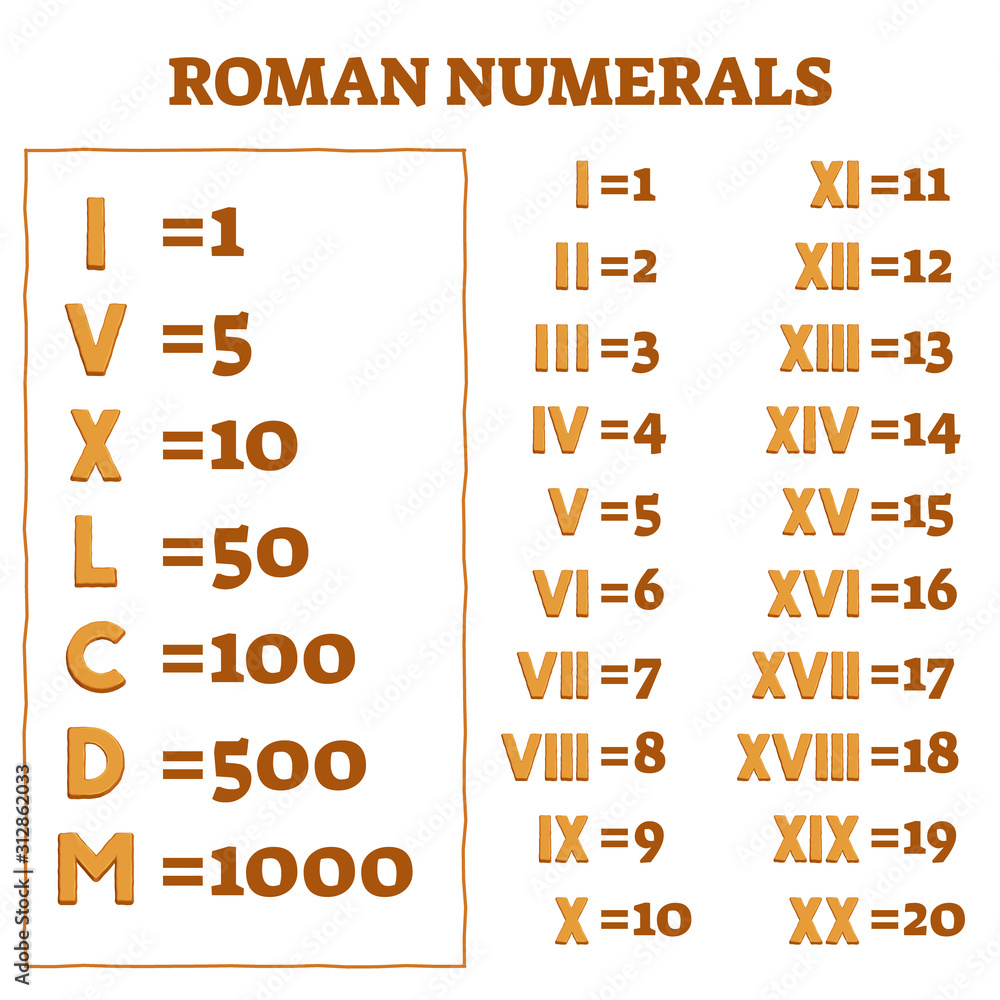
Old Numbers Roman – Roman numerals are utilized in Europe to write numbers. They were the norm until midway through the Middle Ages after they were invented in ancient Rome.
Addition
The Roman numerals, which are a common set for symbols in mathematics, are used. In order to achieve the expected results they must be used in a particular order and are fixed. They are used in order to compute an additive number, without the use of a zero and to represent number such the number of chapters in a book.
Romans employed math to plan their building projects and keep track of military records. The Roman-influenced counting tables were common throughout Europe from the Middle Ages.
As the Romans got older, they could utilize more complicated systems that provided more complex multiplication and division. They employed the decimal system, which consisted of 10 numerals plus four letters. These were the same ones that were used in the creation of the abacus. It was a gadget with glass counters and beads.
One of the most complex systems of computation was the abacus. It was a system of organizing numbers in the order it should. However, this system was not able to accommodate long division.
Subtraction
Roman numerals can be utilized for a variety of reasons. They employ symbols to represent base numbers in an subtractive scheme. These numbers are typically employed to show hierarchical connections, and signify dates. These numbers can be used in photography, but they are also used to denote different brightness levels.
Romans were able to count numbers with an Abacus. The abacus they used was a popular object. The device was utilized by the Romans for military accounting and counting. Three unciae, for example could be a representation of one quarter of the Roman army.
The Roman numeral system served one main purpose: to facilitate multiplication, addition, and multiplication. In order to accomplish this the letters C-X were used. The symbols could not be altered unlike the current Abacus.
It was also straightforward to subtract numbers with the Roman numerals. Roman numerals demand that the letter lower is followed by a higher value that is at least 10 times larger. Additionally, the letter’s initial value should be lower than the one that is replaced.
Stairsteps pattern from the fracture
Numerous patterns and shapes that resemble fractals can also be discovered in nature, such as the Roman numerals-based steps. Designers, architects, and engineers have utilized fractal geometry to design complex digital artworks.
Recursion is a mathematical concept which creates fractions. It is a method for solving problems. To construct the Dragon’s Curve, you would start with U (square-based) and repeat the circle four times. Each iteration increases the distance between the square’s sides.
Recursive building is also illustrated through the Sierpinski triangular. This triangle is formed from four smaller triangles with the same form.
Fractal concepts were initially linked to the physical modeling methods. However, it is possible to copy vegetable shapes today due to technologically advanced computational algorithms.
One of the main advantages is the fine-grained nature of fractal branching. It features a zoom symmetry and a structural appearance.
Different professionals can offer various reasons for branches to appear like trees. While the basic concept behind a tree’s photosynthesis is sunlight, there are other reasons for why it branches. Furthermore, trees with branches can provide numerous mechanical advantages.
Origins
Roman numerals first appeared in Rome the city of ancient state. They are used in various ways today. They can also be used to date media. They are also mentioned in the names of popes or the kings.
Roman numerals could be taken from the tally sticks that were used in the Roman Empire by shepherds to keep track of their flocks. However, it’s not known where they came from. Depending on the type, the notch that represents the 10th sheep will be an “X” form.
These images continued to be used for a long time after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. Later, the Arabic systems replaced them. After their introduction to Europe during the 11th century the numbers began to gain wide acceptance in the 16th century.
Roman numerals continue to be employed, even though they are simpler to recall as compared to the Arabic system. They appear frequently in clocks, sporting events, and even the names and addresses of popes.