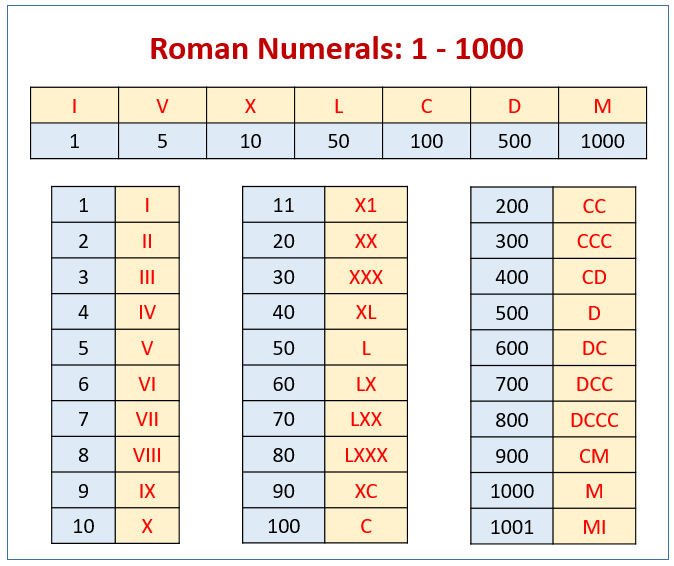
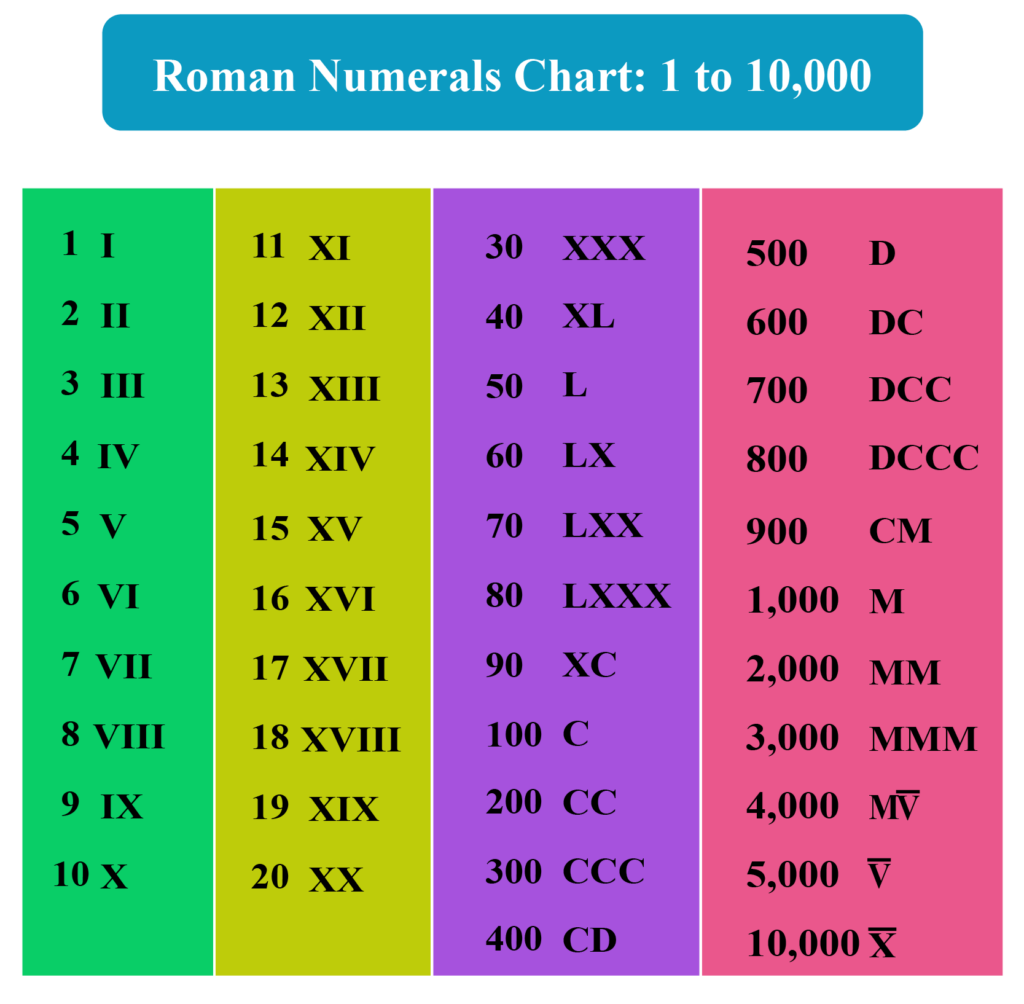
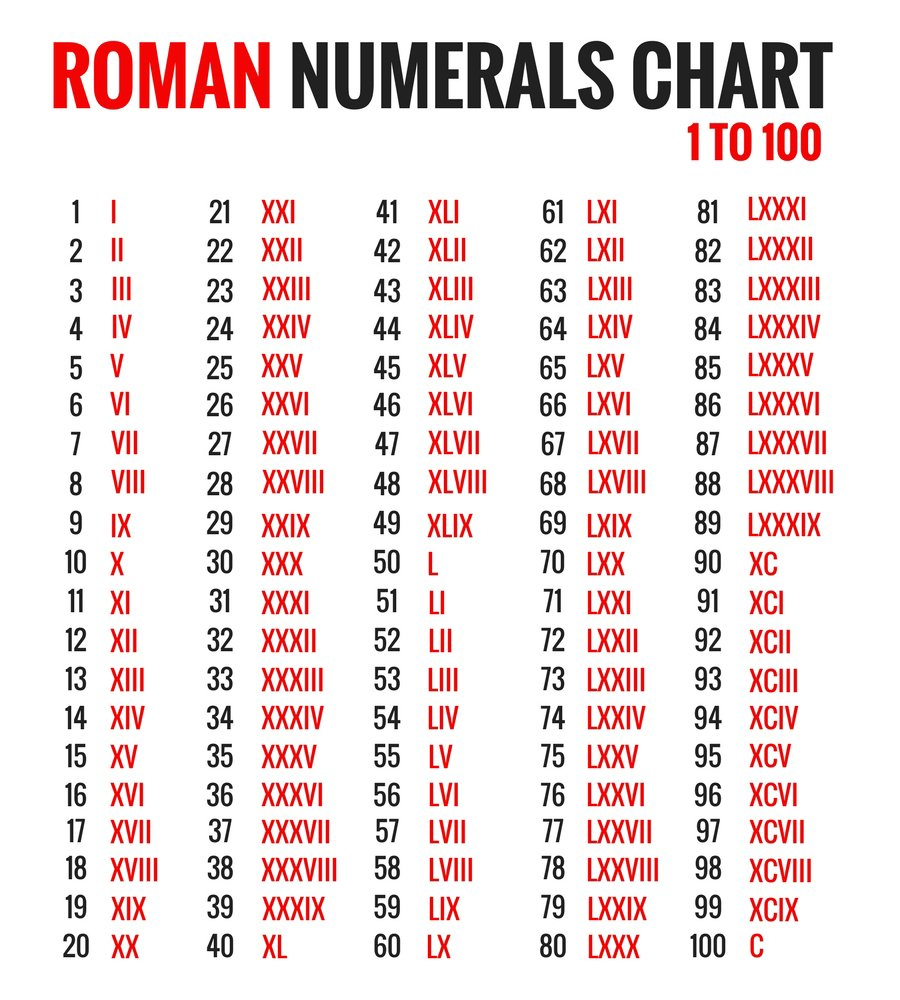
Roman Numberals Chart – Roman numerals used in Europe are used extensively for writing numbers. They were the standard until midway through the Middle Ages after they were created in the early days of Rome.
Additional
The Roman numerals, a traditional set of mathematical symbols are employed. The letters must be put in the proper order to produce the desired results. They are utilized to calculate an additional number system that does not use a zero to represent numbers, for instance chapters in books.
Romans employed maths to keep track of their records of military. Roman-inspired count boards were utilized throughout Europe until the Middle Ages.
As they aged, the Romans could use an advanced system that included more advanced multiplication and division processes. They used a decimal system consisting of four letters plus ten numerals. They were also employed in the development of the calculator. It was a gadget with glass counters, beads and an electronic calculator.
One of the most complicated methods of computation was the abacus. It was a system of organizing numbers in the order it should. But, this method was not able to accommodate long division.
Subtraction
Roman numerals can be utilized for many purposes. They make use of symbols to represent a base number in a subtractive scheme. These numbers are commonly used to count, denote the hierarchy of connections, as well as to represent dates. They also are used in photography to indicate different levels of brightness.
Romans employed an abacus to symbolize numbers. The abacus they used reminded us of the object we have all seen. The Romans used this tool for military accounting in addition to counting. For instance, three unciae can be one-quarter of the Roman army.
The main purpose of the Roman numeral system was to simplify multiplication and addition. In order to accomplish this the letters C-X were used. However, the symbols are locked and couldn’t be altered, unlike the modern Abacus.
Additionally subtraction of numbers was easy thanks to Roman numerals. Roman numerals need to follow these rules The letter with a lower value must be followed immediately by a number at minimum 10x greater. The letter’s value should be lower than the original number.
Stairstep pattern is a fractal
There are several fractal-like forms and patterns found in nature, such as the stairstep patterns in Roman numerals. Designers, engineers, architects and others have employed fractal geometrics to design intricate digital designs.
Recursion is an mathematical concept that generates and sustains fractures. It’s a way to tackle issues. For example, you begin by using the square-based letters U and then multiply the area by four to create the Dragon’s Curve. Each time, you increase the distance between square’s sides.
Another illustration of recursive construction is the Sierpinski triangle. The triangle is comprised of four triangles, each of which has the same form.
Fractals originated as physical modeling techniques. But, it’s possible to replicate vegetable forms today thanks to the advancements in computational algorithms.
One of the greatest benefits is the fine-grained, intricate nature of natural fractal branching. It displays zoom symmetry in addition to its structural appearance.
Different professions have their own explanations for branches that look like trees. However, the basic idea is that photosynthesis happens in sunlight. A branching structure like a tree is mechanically advantageous.
Origins
Rome as a city-state from the past was the place the place where Roman numerals first appeared. Numerous uses for them exist today. They can be used to establish dates for media, among other things. They are also in the names of kings and popes.
Roman numerals were believed to be derived from tallysticks utilized by Roman Empire shepherds to keep track of their flocks. However their origins aren’t known. Depending upon the type of sheep, the tenth would have an “X”-shaped notch on a wooden tally stick.
Images of these were utilized in the aftermath of the demise of the Western Roman Empire. But later the Arabic system started to take their place. These numbers were accepted widely throughout Europe by the end of the sixteenth century.
Roman numerals are still being employed, even though they are easier to recall as compared to the Arabic system. They are frequently used in sports events, clocks, and the names popes or kings.