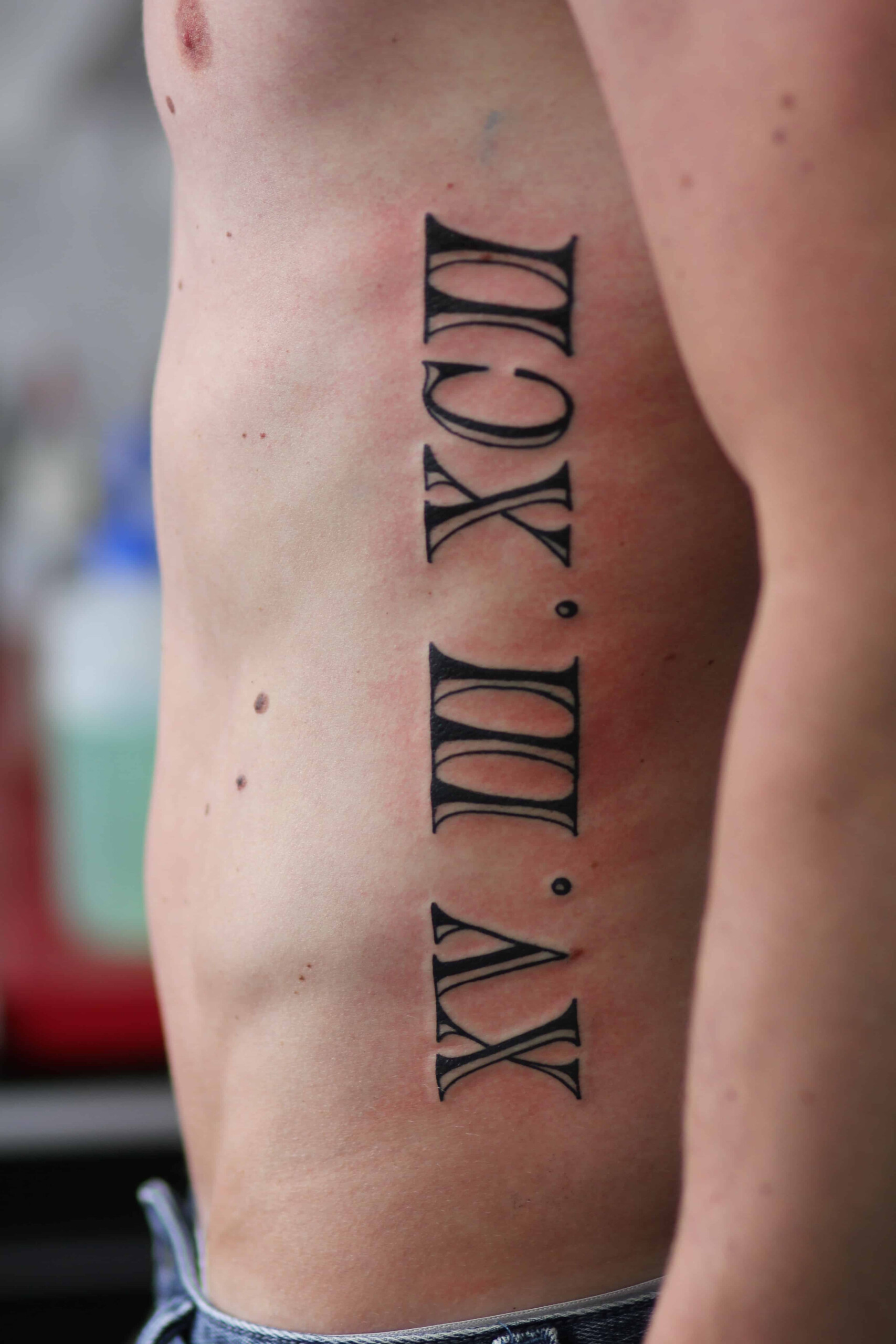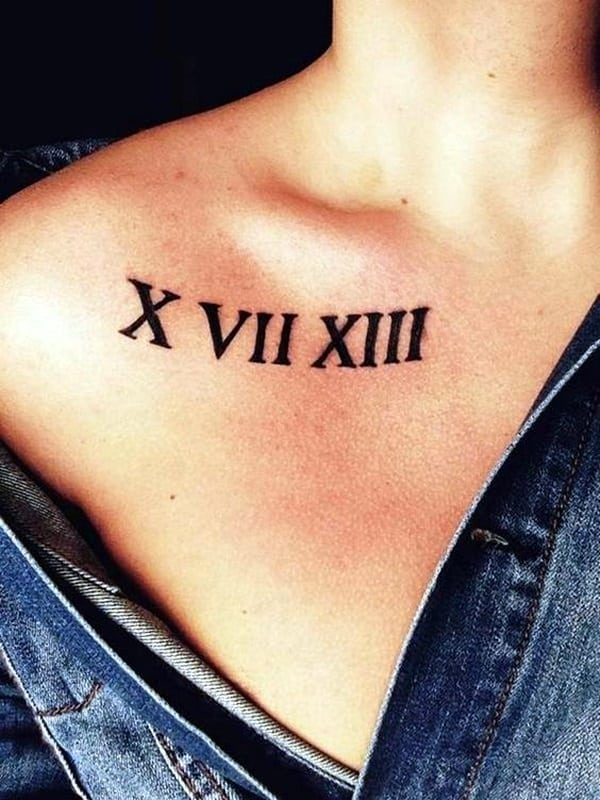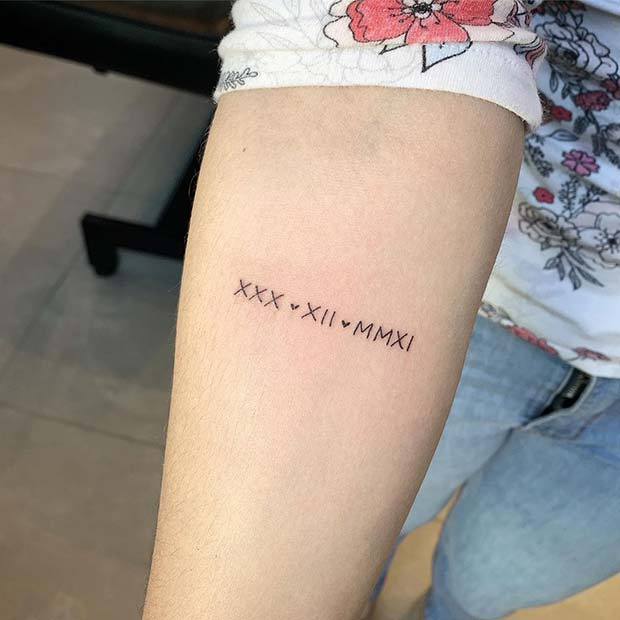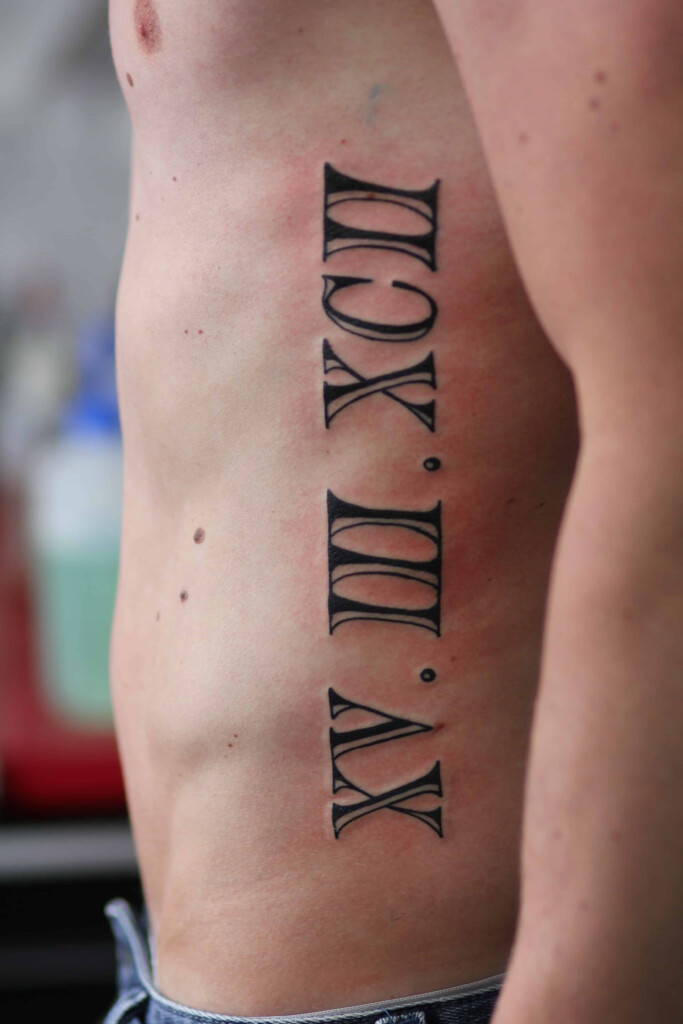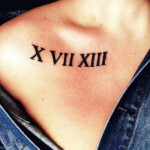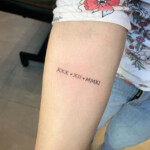Tattoo In Roman Numbers – Roman numerals used in Europe are commonly used for writing numbers. They were the standard for writing numbers prior to the end of Middle Ages.
In addition
The Roman numerals represent an array of symbols that are used for mathematics. Roman numerals are the common set of symbols in mathematics. They should be utilized in the correct order and set to give the desired results. They are employed to compute an additive number, without the use of a zero or to represent a number, such as the number of chapters in a book.
Romans utilized math to manage their construction projects and keep the track of military records. Roman-inspired counting boards were widely used in Europe up until the Middle Ages.
As the Romans became more advanced and advanced, they could utilize a more complicated system that was more sophisticated in its multiplication and division processes. They used a decimal scheme using four letters, ten numbers. These were the same people who made the abacus – an instrument that has glass counters and beads.
The abacus, which organized numbers left to right in the way it was supposed to be it was among the most complicated computational systems. But, this method did not allow for long division.
Subtraction
Roman numerals are used for numerous uses. They use symbols to represent the base number in subtractive systems. These numbers are usually utilized to indicate and count hierarchical connections. These numbers are also used in photography, however, to signify different levels of brightness.
Romans represented numbers with an Abacus. Their abacus resembled that of a popular item. It was used for military accounting, as well as counting by the Romans. Three unciae could be used to represent 25 percent of the Roman army.
The primary function of the Roman numeral system was to facilitate multiplication and addition. To achieve this it was the use of the letters C & X were used. The symbols couldn’t be changed unlike the contemporary abacus.
It was also straightforward to subtract numbers with the Roman numerals. Roman numerals require that the lower letter is followed by a letter that is at minimum 10 times bigger. Additionally, the letter’s initial value should be lower than the new one.
Stairstep pattern as an fractal
There are numerous designs and patterns that are fractal in nature. Engineers, architects and designers have used fragmental geometry in their designs to create intricate digital artifacts.
Recursion is a mathematical concept which creates and keeps fractals. This is a method to tackle problems. For example, you begin by using the square-based letters U and repeat the region by four, creating the Dragon’s Curve. With each iteration you expand the area between the two sides of the square.
Another instance of recursive construction can be seen in the Sierpinski triangle. The triangle is comprised of four triangles having similar shapes.
Fractal theories were initially tied to the physical modeling methods. It is now possible to duplicate vegetable forms today thanks to the advancements in computational algorithms.
One of its main benefits is the fine-grained nature of fractal branched in nature. It is also known due to its zoom symmetry.
Different fields have different explanations for branches that look like trees. But, sunlight is the only element that trees require to produce photosynthesis. A tree that has branches may have many mechanical benefits.
Origins
Roman numerals first appeared in Rome which was a city-state from the past. They have many uses in our modern world. They are utilized as an example to determine the date of media. They are also included in the names of kings and popes.
Roman numerals could have been taken from tallysticks used by shepherds to keep track of their flocks during the Roman Empire. But their precise origins remain an unanswered question. The tenth sheep would have an “X”-shaped notch on the tally stick, according to the type.
The images remained in use even after the Western Roman Empire was destroyed. Later, however, the Arabic system took their place. The numbers were widely accepted throughout Europe towards the end of the sixteenth century.
Even though the Arabic system is simpler to grasp, Roman numerals still have an important place in the modern world. They appear in a lot of clocks, sports events, and the addresses and names of popes.