Whats The Difference Between Roman & Arabic Numbers – In Europe, Roman numerals are typically used to write numbers. They were the preferred method of writing numbers prior to the end of Middle Ages.
Additional
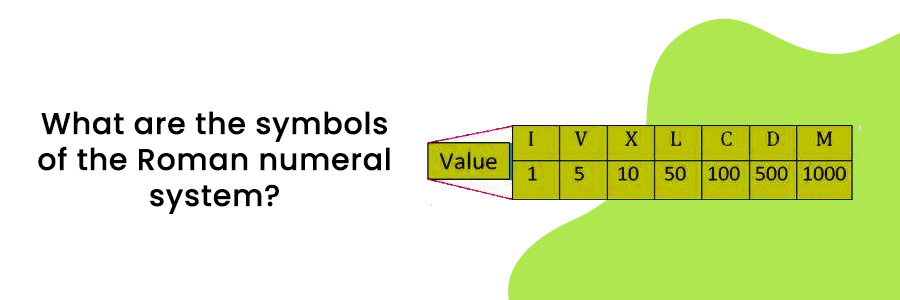
The Roman numerals are an established set of mathematical symbols. The letters need to be put in the proper sequence to yield the expected results. They are used to calculate an additive number system without utilizing a zero and to represent a number, like a chapter number.
Romans employed math to manage military records and organize construction projects. Roman-inspired counting boards were popular in Europe from the Middle Ages.
As the Romans grew in the years of their lives, they created an elaborate system that enabled more division and multiplication. They employed decimal numbers that comprised 10 numerals and four letters. The same numbers were used to make the abacus, which was a device made of counters made of glass that had beads.
The abacus system, which organized numbers left to right in the way it was supposed to be, was one of the most complex systems of computation. This method was not effective for long division.
Subtraction
There are a variety of applications for Roman numerals. They make use of symbols to represent a base number in a subtractive system. They are typically used to represent numbers, to indicate hierarchical connections as well as to signify dates. These numbers are also used in photography, but they are also used to signify different levels of brightness.
Romans used to represent numbers with an Abacus. Their abacus was similar to a famous object. The device was utilized for military accounting and also for counting by the Romans. For instance three unciae could be a quarter of the Roman army.
The Roman numerals were designed to facilitate multiplication. The letters C and X were used for this. The symbols were fixed and could not be changed, unlike the modern abacus.
It was also simple to subtract numbers using Roman numerals. Roman numerals need to follow these rules that a letter with lower value must be followed immediately by a number at minimum 10x greater. The value of a letter must be less than the initial number.
Stairstep pattern, similar to an fractal
Many patterns and forms that resemble fractals can also be seen in nature, such as the Roman numerals-based stairstep patterns. Designers, architects, and engineers have utilized fractal geometry to design complex digital artworks.
Recursion is a mathematical concept which creates and keeps fractals. This is a technique to solve problems. To construct the Dragon’s Curve the process begins with U (square-based) and repeat the circle four times. Each time you repeat the process, the area increases between square’s edges.
Another instance of recursive construction can be seen in the Sierpinski triangle. The triangle is comprised of four smaller triangles each with the same overall shape.
Fractals were originally linked to physical techniques for modeling. But, the latest algorithms for computation allow to replicate the forms of vegetables.
One of the main advantages is the fine-grainedness of fractal branching. It displays zoom symmetry, as well as its structure.
Different fields of study can provide different explanations why branches look like trees. However, sunlight is the only requirement for a tree to photosynthesise. There are also mechanical benefits for a tree’s branching system.
Origins
Roman numerals are a result of Rome, an ancient city. They are used for a variety of functions in the contemporary world. They are utilized, for instance to date the media. They also are in the names of popes.
Roman numerals were believed to have come from tallysticks that were used by Roman Empire shepherds to keep track of their flocks. However their origins are not known. The tenth sheep would be a tally stick with an “X”-shaped notch on the tally stick, dependent on the type.
These images remained in use for a long time after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. Then they were replaced by the Arabic system was introduced to replace them. In the 16th century, these numbers were gaining widespread acceptance after being brought into Europe during the 11th century.
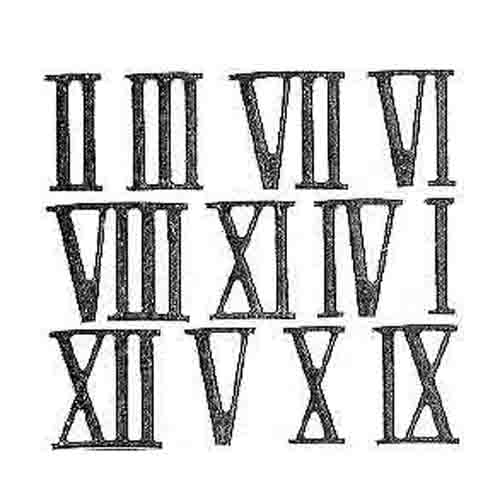
Roman numerals are still used in the present even though the Arabic system is considered to be simpler to use. They are often used in clocks, sporting events, and the addresses and names of popes.